Repository và Unit of Work Pattern
Repository, hiểu một cách đơn giản, là 1 tầng phân chia giữa Data Access Layer (DAL) và Bussiness Logic Layer.
Unit of Work là một kỹ thuật để đảm bảo tất cả các request tới database mà có liên quan tới nhau đều được thực hiện trên cùng một DbContext
- 1. DbContext của Entity Framework Core
- 2. Repository
- 3. Generic Repository
- 4. Tạo class Unit of Work
- 5. Tổng kết
1. DbContext của Entity Framework Core
“Trước giờ xài mà có để ý DbContext là gì đâu” -> đây chắc là tình trạng chung của kha khá công nghệ liên quan tới .NET, khi mà mọi thứ đã được xây dựng sẵn, và bạn chỉ có nhiệm vụ … xài
DbContextlà một thực thể đại diện cho một phiên làm việc với database, dùng để query và lưu dữ liệu của bạn
Vì nó chỉ đại diện cho 1 phiên làm việc, trong ASP.NET, mỗi khi có 1 request mới từ browser, 1 DbContext mới sẽ được tạo ra, và sẽ bị dispose khi return response cho browser
Thông thường, bạn sẽ kế thừa lại từ DbContext, nhét thêm các DbSet vào, từ đó mới query các kiểu được
Bạn có thể tham khảo thêm về cách thiết lập
DbContextở đây, mục 3.2
1.1. DbContext Tracking
Để đảm bảo tính toàn vẹn dữ liệu, DbContext dùng 1 cơ chế gọi là tracking.
Khi bạn thay đổi 1 record (thêm, xóa, sửa), thì thay đổi đó ko được đưa xuống database ngay, mà sẽ còn vương vấn lại. DbContext sẽ theo dõi sự thay đổi này.
Cho tới khi bạn đã thực hiện tất cả các thay đổi cần thiết, rồi gọi yourDbContext.SaveChanges(), thì lúc này, những thay đổi được track sẽ được ship xuống database.
Vậy tất cả những điều này liên quan gì tới Repository và Unit of Work? DbContext là một implement của Repository và Unit of Work, chỉ có điều nó nằm sâu trong framework, còn implement của bạn sẽ nằm ở application
2. Repository
Có cái sơ đồ hay ho sau
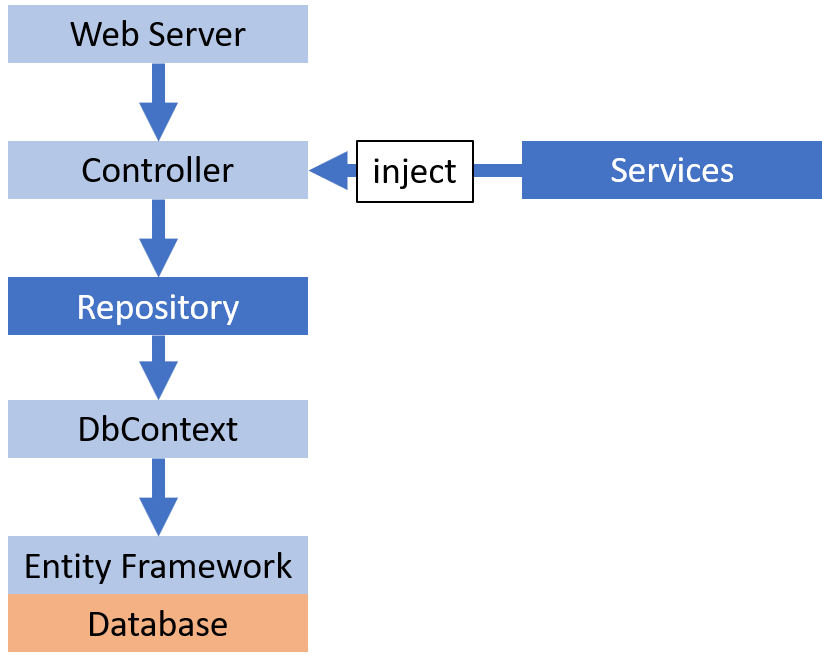
Bạn có thể đọc thêm về các services được inject tại bài viết Dependency Injection trong ASP.NET Core
Vậy đóa, Repository đóng vai trò là 1 lớp trung gian giữa Bussiness Logic Layer (controllers và services) và Data Access Layer (các DbContext)
2.1. Lý do
Tách việc xử lý logic và việc truy cập database
- Dễ trace bug
- Dễ unit test
- Dễ thay đổi logic hoặc database
Gom chung nhìu tác vụ cơ bản về 1 chỗ
- Ko phải viết đi viết lại 1 tác vụ nhiều lần
2.2. Implement
Cụ tỉ, Repository sẽ có các nhiệm vụ: Liệt kê danh sách các record - Lấy 1 record - Thêm - Xóa - Sửa 1 record
Bài toán: quản lý học sinh
Tạo interface
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using ContosoUniversity.Models;
namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL
{
public interface IStudentRepository : IDisposable
{
IEnumerable<Student> GetStudents();
Student GetStudentByID(int studentId);
void InsertStudent(Student student);
void DeleteStudent(int studentID);
void UpdateStudent(Student student);
void Save();
}
}Đoạn code trên khai báo một bộ CRUD (Create - Read - Update - Delete) kinh điển
Tạo class implement
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Data;
using ContosoUniversity.Models;
namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL
{
public class StudentRepository : IStudentRepository, IDisposable
{
// SchoolContext kế thừa từ DbContext, và có thêm DbSet<Student>
private SchoolContext context;
public StudentRepository(SchoolContext context)
{
this.context = context;
}
public IEnumerable<Student> GetStudents()
{
return context.Students.ToList();
}
public Student GetStudentByID(int id)
{
return context.Students.Find(id);
}
public void InsertStudent(Student student)
{
context.Students.Add(student);
}
public void DeleteStudent(int studentID)
{
Student student = context.Students.Find(studentID);
context.Students.Remove(student);
}
public void UpdateStudent(Student student)
{
context.Entry(student).State = EntityState.Modified;
}
public void Save()
{
context.SaveChanges();
}
private bool disposed = false;
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!this.disposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
context.Dispose();
}
}
this.disposed = true;
}
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
}
}Inject repository này vào Controller hoặc Service (nhớ khai báo nó trong Startup.cs trước nhóe)
public class StudentController
{
private readonly IStudentRepository _studentRepository;
public StudentController(IStudentRepository studentRepository)
{
_studentRepository = studentRepository
}
}2.3. Performance Hit
Entity Framework khi query một record hoặc 1 bộ record nào đó trong database, nó sẽ trả về dạng IQueryable. Chỉ khi nào bạn gọi .ToList();, thì câu lệnh SQL mới được sinh ra và gửi tới database.
Trong StudentRepository ở trên, nếu bạn muốn filter 1 list các student có tên là “ABC”, thì sẽ phải code trong controller như sau
public IActionResult GetStudents(string name)
{
// SQL đã được sinh ra, toàn bộ student trong db đã được trả về và lưu trong memory
var allStudents = _studentRepository.GetStudents();
// filter này chỉ thực hiện việc filter trên memory
var filteredStudents = allStudents.Where(x => x.Name.Contains(name));
return View(filteredStudents);
}Đây là 1 code rất tệ khi mà student có hàng triệu record, trong khi bạn chỉ cần 1 số ít các record mà thôi.
Ở phần sau, bạn sẽ biết cách fix cho vấn đề này, đồng thời implement 1 generic repository cho các tác vụ CRUD cơ bản
3. Generic Repository
Về cơ bản, ta sẽ dùng kiểu khai báo generic class của C# để implement generic repository
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Entity;
using ContosoUniversity.Models;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL
{
public class GenericRepository<TEntity> where TEntity : class
{
// SchoolContext được kế thừa từ DbContext
internal SchoolContext context;
// Generic repository này sẽ hoạt động dựa trên entity được truyền vào khi đăng ký trong Startup.cs
internal DbSet<TEntity> dbSet;
public GenericRepository(SchoolContext context)
{
this.context = context;
this.dbSet = context.Set<TEntity>();
}
// Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter: cho phép bạn truyền vào một filter expression dạng LINQ
public virtual IEnumerable<TEntity> Get(
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter = null,
Func<IQueryable<TEntity>, IOrderedQueryable<TEntity>> orderBy = null,
string includeProperties = "")
{
IQueryable<TEntity> query = dbSet;
// Query là 1 dạng IQueryable, chỉ được thực thi khi cần giá trị list
if (filter != null)
{
query = query.Where(filter);
}
// Tiếp theo, nó sẽ kèm theo các property cần thiết khi người dùng chỉ định
foreach (var includeProperty in includeProperties.Split
(new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries))
{
query = query.Include(includeProperty);
}
// Sau cùng, nó thực thi bằng cách translate thành câu lệnh SQL và gọi xuống database
if (orderBy != null)
{
return orderBy(query).ToList();
}
else
{
return query.ToList();
}
}
// trong asp.net, Id cho 1 object có thể là GUID hoặc int
public virtual TEntity GetByID(object id)
{
return dbSet.Find(id);
}
public virtual void Insert(TEntity entity)
{
dbSet.Add(entity);
}
// trong asp.net, Id cho 1 object có thể là GUID hoặc int
public virtual void Delete(object id)
{
TEntity entityToDelete = dbSet.Find(id);
Delete(entityToDelete);
}
public virtual void Delete(TEntity entityToDelete)
{
if (context.Entry(entityToDelete).State == EntityState.Detached)
{
dbSet.Attach(entityToDelete);
}
dbSet.Remove(entityToDelete);
}
public virtual void Update(TEntity entityToUpdate)
{
dbSet.Attach(entityToUpdate);
context.Entry(entityToUpdate).State = EntityState.Modified;
}
}
}4. Tạo class Unit of Work
Unit of Work chỉ có 1 nhiệm vụ duy nhất, đảm bảo tất cả các repository của bạn đều dùng chung một DbContext. Bằng cách này, khi thực hiện xong tất cả các tác vụ thay đổi database, bạn chỉ cần gọi DbContext.SaveChanges() 1 lần duy nhất, và các thay đổi đó sẽ được lưu lại trong database
using System;
using ContosoUniversity.Models;
namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL
{
public class UnitOfWork : IDisposable
{
private SchoolContext context = new SchoolContext();
private GenericRepository<Department> departmentRepository;
private GenericRepository<Course> courseRepository;
// Kiểm tra xem repository đã được khởi tạo chưa
public GenericRepository<Department> DepartmentRepository
{
get
{
if (this.departmentRepository == null)
{
this.departmentRepository = new GenericRepository<Department>(context);
}
return departmentRepository;
}
}
// Kiểm tra xem repository đã được khởi tạo chưa
public GenericRepository<Course> CourseRepository
{
get
{
if (this.courseRepository == null)
{
this.courseRepository = new GenericRepository<Course>(context);
}
return courseRepository;
}
}
public void Save()
{
context.SaveChanges();
}
private bool disposed = false;
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!this.disposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
context.Dispose();
}
}
this.disposed = true;
}
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
}
}Bước tiếp theo là thay đổi code của controller để sử dụng class UnitOfWork vừa mới khởi tạo
// Lấy data
var courses = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Get(includeProperties: "Department");
// Lấy và order data
var departmentsQuery = unitOfWork.DepartmentRepository.Get(orderBy: q => q.OrderBy(d => d.Name));
// Insert
var course = new Course();
course.Name = "Test";
...
unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Insert(course);
unitOfWork.Save();
// Hủy
unitOfWork.Dispose();5. Tổng kết
Vậy là bạn đã hiểu khái niệm và cách khai báo Repository và Unit of Work pattern. Bạn cũng đã biết cách sử dụng lambda expression để query các data thỏa điều kiện mong muốn thông qua interface IQueryable. Chúc vui :D